Step 1: Complete the American Heart Association online course.
Step 2: Perform skills testing in one of our 65 local offices.
Step 3: Receive the American Heart Association card same day.

Basic Life Support
Online Course: 1-2 hours
Skills Testing: 30 minutes
100% Pass Rate Guaranteed
Lowest Prices In California
Receive Card On Class Day
Thousands of 5 Star Reviews
CE Credits to CA Dentists
Advanced Cardiac Life Support
Online Course: 2-3 hours
Skills Testing: 30 minutes
100% Pass Rate Guaranteed
Lowest Prices In California
Receive Card On Class Day
Thousands of 5 Star Reviews
Some Professions: 2-3 CEU

Pediatric Advanced Life Support
Online Course: 2-3 hours
Skills Testing: 30 minutes
100% Pass Rate Guaranteed
Lowest Prices In California
Receive Card On Class Day
Thousands of 5 Star Reviews
Some Professions: 3.75-5 CEU

Neonatal Resuscitation Program
Online Course: 2-3 hours
Skills Testing: 3 hours
100% Pass Rate Guaranteed
Lowest Prices In California
Receive Card On Class Day
Thousands of 5 Star Reviews
Some Professions: 4 CEU
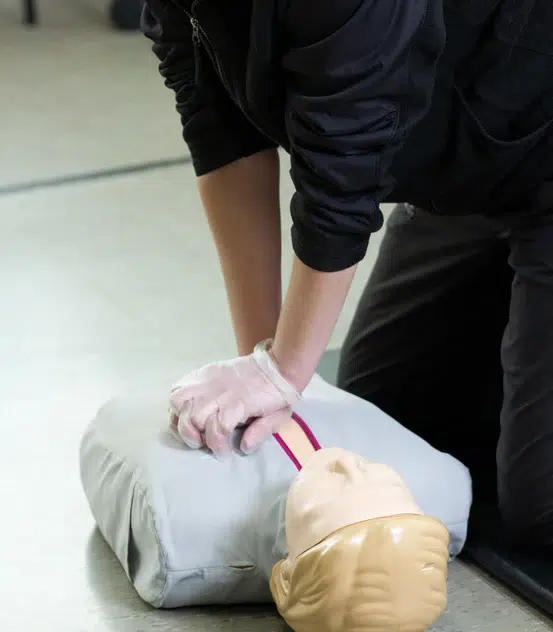

Audience: General public
Topics: CPR for all age groups, AED use, bleeding, epi-pen, etc
Online Session: 1 Hour
Skills Testing: 30 minutes
Card: Safety Training Seminars
Certification: Valid 2 years

Audience: General public
Topics: CPR for all age groups, AED use, bleeding, epi-pen, etc
AHA Online Course: 1-2 Hours
Skills Testing: 30-45 minutes
Card: American Heart Association
Certification: Valid 2 years

Audience: CA childcare providers
Topics: CPR for all age groups, AED use, bleeding, epi-pen, etc
AHA Online Course: 1-2 Hours
Skills Testing: 30-45 minutes
Card: American Heart Association
Certification: Valid 2 years

Audience: Childcare providers
Topics: Lead poisoning, nutrition, infectious disease,etc
Zoom Course: 8 Hrs (state law)
Skills Testing: 30-45 minutes
Card: EMSA Health & Safety
Certification: No expiration
Safety Training Seminars offers the lowest priced American Heart Association courses in California - backed by the low price guarantee.
Safety Training Seminars issues the American Heart Association card on the day of the class. Some companies takes 2 weeks or longer to issue the cards.
Safety Training Seminars is an official American Heart Association Training Center (20784) that is licensed to teach in every state in the US.
Safety Training Seminars has excellent customer service and our staff answers calls and email every day (including weekends) from 7 am to 7 pm.
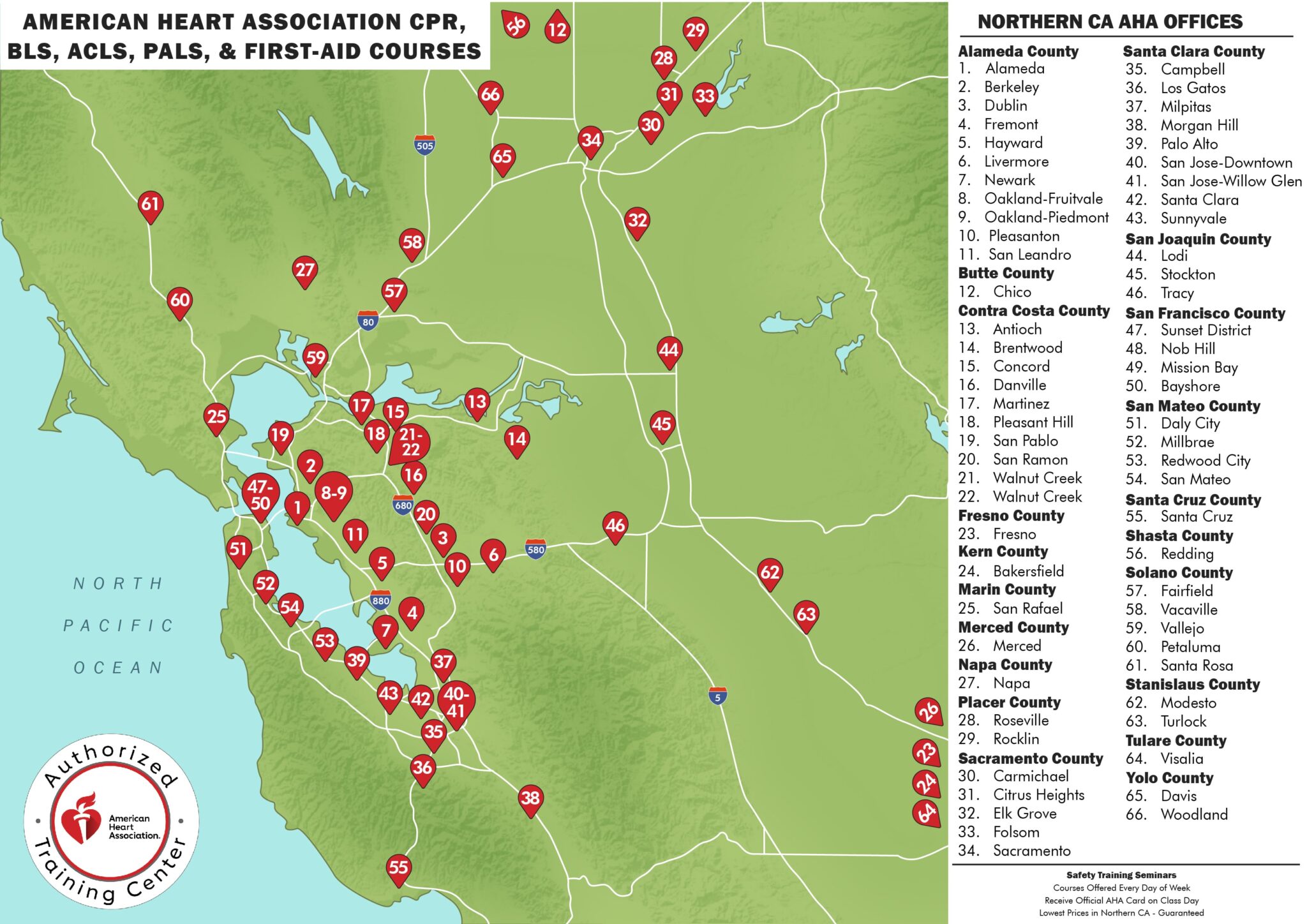
Safety Training Seminars has over 70 CPR offices located throughout California. We are sure you can find a location to renew your card near you.
Safety Training Seminars has thousands of 5 star reviews. Our clients come back to us year after year since we provide excellent customer service.
Safety Training Seminars is a local woman-owned business. Laura Seidel cares deeply about providing great service to her customers.
Safety Training Seminars offers convenient options to attain CPR certification cards by offering courses every day of the week including weekends & evenings.
EXCELLENTTrustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I really appreciated the instruction and feedback provided by the trainers during the BLS class, earning me comprehensive and coveted BLS certification that I'm confident will serve me well in any emergency situation.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I was really impressed with the BLS class I took at Safety Training Seminars, which not only effectively trained me in life-saving skills but also gave me reassurance in earning my BLS certification.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Class was excellent! Easy instructions, clean equipment and facility. Thank you!Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I recently completed the BLS Class at Safety Training Seminars and left feeling highly confident in my ability to respond to emergency situations with the knowledge and skills I gained. Quick, easy, and seamless course.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I recently attended Safety Training Seminars for BLS certification and was very impressed with the experience, the instructor provided clear and concise instructions that made the material easy to understand, making me feel confident and prepared for my certification exam.Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. Good place, good manikins, and the online courses for ACLS/PALS are really helpful! Highly recommend!Trustindex verifies that the original source of the review is Google. I’ve taken my CPR/First Aid/EMSA/BLS certification training at Safety Training Seminars for many years. This is a top notch organization!! I know I can count on the instructors at Safety Training Seminars to expertly guide me through the CPR and First-aid class, providing clear instructions and hands-on training to ensure I receive the highest quality of education, ultimately resulting in a well-rounded understanding of lifesaving techniques necessary for BLS and EMSA certification. In prior years, I attended classes in person. I was a bit hesitant to take the hands-on portion in a virtual classroom this year. Happily, it was just as helpful and easy to navigate as the in-person was!! Georgia, an actual live trainer on Skype, was fantastic! Everything was clear, smooth, and thoughtful! Thank you to the dedicated women at Safety Training Seminars!!
The American Heart Association RQI (Resuscitation Quality Improvement) program is the leading, cutting-edge, and efficient way for medical and healthcare professionals to earn their official AHA BLS, ACLS, and PALS certification cards.
1️⃣ Complete the online course at your convenience (a few hours).
2️⃣ Perform a skills test using a Voice-Assisted Manikin (VAM).
3️⃣ Receive your certification card on the same day as your class.
Safety Training Seminars is a woman-owned American Heart Association (AHA) Training Center, offering high-quality BLS, ACLS, PALS, CPR, and First Aid courses in California.
We provide AHA-certified BLS, ACLS, PALS, CPR, and First Aid courses every day in California, making training easily accessible.
We offer the most competitive prices for CPR in California, backed by our Low Price Guarantee.
If you’re searching for life-saving certification courses near you, the American Heart Association (AHA) offers a range of essential training programs designed for both healthcare professionals and the general public. Whether you’re looking to fulfill job requirements or simply want to be prepared in an emergency, AHA-certified CPR, BLS, ACLS, PALS, and First Aid courses are widely available at local training centers across the country.
CPR (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) is a foundational skill that everyone should know. AHA CPR courses teach you how to perform chest compressions and rescue breaths for adults, children, and infants, equipping you to respond effectively during cardiac or respiratory emergencies.
BLS (Basic Life Support) is designed specifically for healthcare providers and first responders. This BLS course includes high-quality CPR training, use of an AED, and team dynamics in medical emergencies. It’s a required certification for many medical professionals, including nurses, EMTs, and dental staff.
ACLS (Advanced Cardiovascular Life Support) is intended for advanced healthcare providers who manage cardiovascular emergencies such as cardiac arrest and stroke. The course covers advanced airway management, ECG interpretation, and pharmacology.
PALS (Pediatric Advanced Life Support) focuses on emergency care for infants and children. It’s essential for pediatricians, emergency room staff, and paramedics who handle critical pediatric cases.
First Aid courses cover how to manage common injuries and medical emergencies such as bleeding, burns, allergic reactions, and fractures. This training is valuable for teachers, coaches, parents, and anyone wanting to improve their emergency readiness.
New Office Openings
We are constantly opening up new CPR offices to better serve our clients. Over the past few months, we have opened a new BLS certification school in Fresno, Bakersfield, and Redding.
These AHA-certified classes are offered regularly at our over 65 locations in California. Our offices are located in small cities and large metro areas, such as Sacramento, San Francisco, Oakland, and San Jose. Many locations also provide blended learning options with online coursework and in-person skills assessments. Certification cards are valid for two years. Whether you’re a professional or a concerned citizen, these courses empower you to save lives when every second counts.